Of all types of diabetes, Diabetes mellitus (DM), commonly known as just diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level over a prolonged period.
Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst, and increased appetite. If left untreated, diabetes can cause many health complications. Acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperbola, hyperglycemic state, or death.
Serious long-term complications include cardiovascular disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease, foot ulcers, damage to the nerves, damage to the eyes, and cognitive impairment.
Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin or the body’s cells not responding correctly to the insulin produced. There are three main types of diabetes mellitus.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes results from the pancreas’s failure to produce enough insulin due to the loss of beta cells. An autoimmune response causes this loss, and the cause of this autoimmune response is unknown. This form was previously referred to as “insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus” (IDDM) or “juvenile diabetes.”
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes begins with insulin resistance, a condition in which cells fail to respond to insulin appropriately. This form was previously referred to as “non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus” (NIDDM) or “adult-onset diabetes” The most common cause is a combination of excessive body weight and insufficient exercise. As the disease progresses, a lack of insulin may also develop.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is the third main form and occurs when pregnant women without a previous history of diabetes develop high blood sugar levels.
According to Diabetes Research Clinical Practice,
As of 2019, an estimated 463 million people had diabetes worldwide (8.8% of the adult population), with type 2 diabetes making up about 90% of the cases. Rates are similar in women and men. Trends suggest that rates will continue to rise.
Diabetes at least doubles a person’s risk of early death. It is the 7th leading cause of death globally. In 2019, diabetes resulted in approximately 4.2 million deaths. The global economic cost of diabetes-related health expenditure in 2017 was estimated at US$727 billion. In the United States, diabetes cost nearly US$327 billion in 2017.
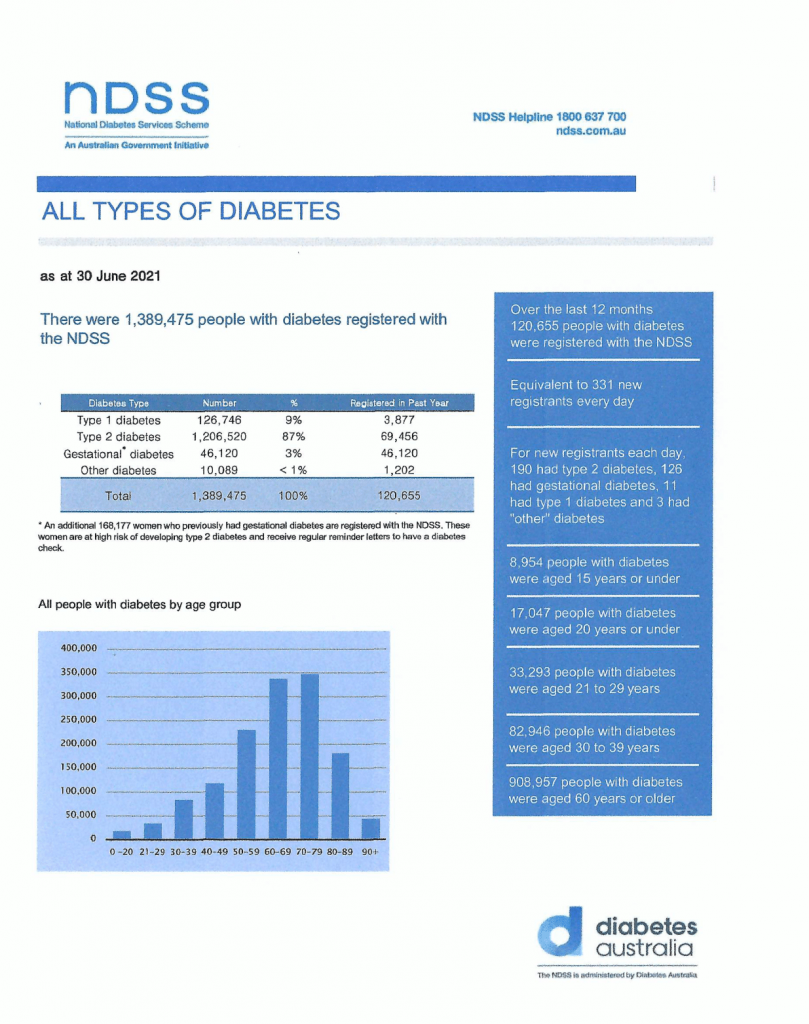
According to NDSS,
[DISPLAY_ULTIMATE_SOCIAL_ICONS]
