Cardiovascular Disease Cardiovascular disease is a type of disease that affects the heart and blood vessels, including the arteries, veins, and capillaries.
It is the leading cause of death in the United States, accounting for nearly 1 in 4 deaths. Common types include coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, stroke, and congestive heart failure.
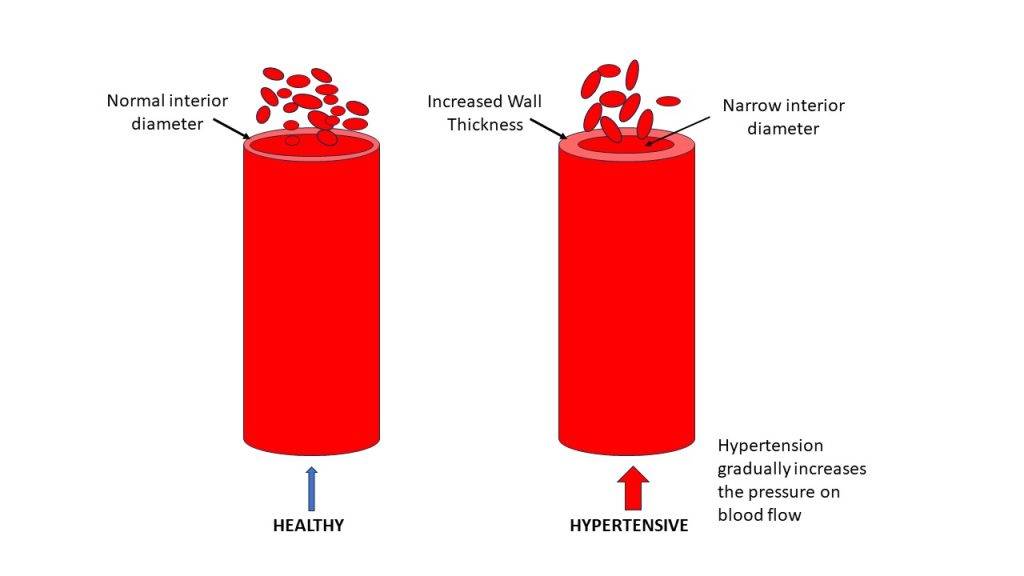
Risk factors include smoking, obesity, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes, and family history.
Treatment includes lifestyle changes, medications, and, in some cases, surgery.
Symptoms are
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Heart palpitations
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Pain or numbness in the extremities
- Difficulty exercising
- Swelling in the feet or ankles
- Heartburn or indigestion
- Cold sweat
- Fatigue
What Can You Do To Improve This Condition
- Eat a healthy diet: Eating a healthy, balanced diet is vital to reducing your risk. Choose nutrient-dense, whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean protein, whole grains, and healthy fats. Avoid processed foods and unhealthy fats.
- Exercise regularly: Cardiovascular exercise helps strengthen your heart and lungs, improve circulation, and reduce your risk of heart disease. Aim for 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Manage stress: Stress can affect your heart health, so finding ways to manage it is essential. Try relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing.
- Quit smoking: Smoking is one of the most critical risk factors. Quitting smoking can reduce your risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Have your blood pressure and cholesterol levels checked regularly and follow your doctor’s instructions for managing them.
- Get regular check-ups: See your doctor regularly for check-ups and screenings. They can help you identify and monitor risk factors.
